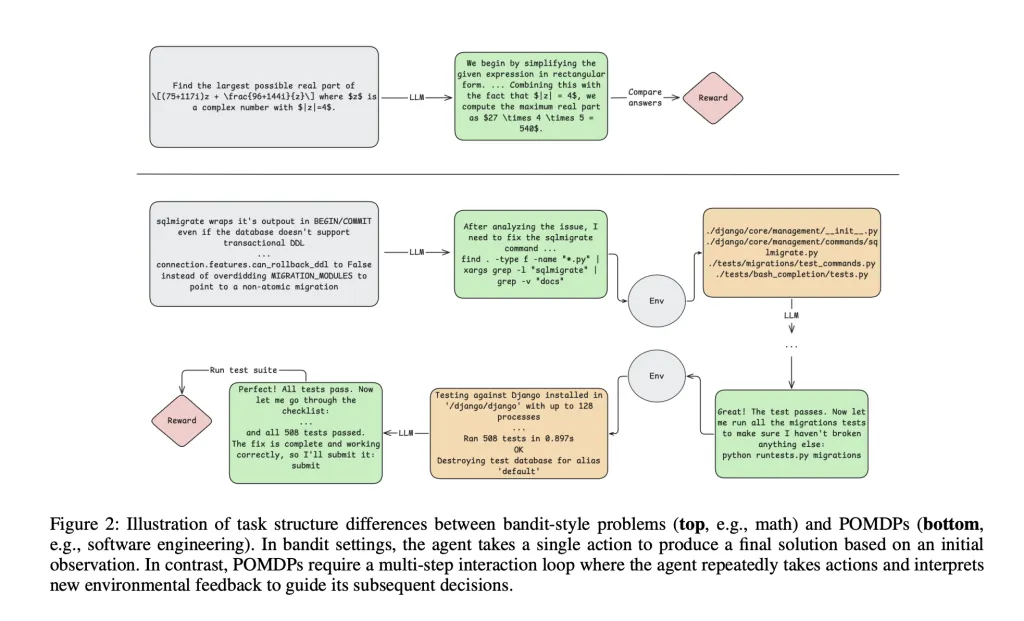
The landscape of software engineering automation is evolving rapidly, driven by advances in Large Language Models (LLMs). However, most approaches to training capable agents rely on proprietary models or costly teacher-based methods, leaving open-weight LLMs with limited capabilities in real-world scenarios. A team of researchers from Nebius AI and Humanoid introduced a reinforcement learning framework for training long-context, multi-turn software engineering agents using a modified Decoupled Advantage Policy Optimization (DAPO) algorithm. The research explains a technical breakthrough in applying reinforcement learning (RL) to open-source LLMs for genuine, multi-turn software engineering tasks—moving beyond the single-turn, bandit-style settings that dominate RL for LLMs today. Beyond Single-Turn Reinforcement Learning RL Most RL methods for LLMs optimize for tasks such as mathematical reasoning or one-shot code generation, where agent actions are rewarded only at the conclusion and environments do not provide intermediate feedback. However, software engineering (SWE) is fundamentally different: it requires agents to operate over long sequences of actions, interpret rich feedback (compiler errors, test logs), and maintain context over hundreds of thousands of tokens—far exceeding typical single-step interaction loops. Core Challenges in RL for SWE Long-Horizon Reasoning: Agents must sustain logical coherence across many steps, often requiring context windows beyond 100k tokens. Stateful Environment Feedback: Actions yield meaningful, non-trivial observations (e.g., shell command outputs, test suite results) that guide subsequent decisions. Sparse/Delayed Rewards: Success signals typically emerge only at the end of complex interactions, complicating credit assignment. Evaluation Complexity: Measuring progress requires full trajectory unrolling and can be noisy due to test flakiness. The Technical Recipe: Modified DAPO and Agent Design The research team demonstrates a two-stage learning pipeline for training a Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct agent: 1. Rejection Fine-Tuning (RFT) The journey begins with supervised fine-tuning. The agent is run across 7,249 rigorously filtered SWE tasks (from the SWE-REBENCH dataset). Successful interaction traces—where the agent passes the environmental test suite—are used to fine-tune the model, particularly masking invalid environment-formatting actions during training. This alone boosts baseline accuracy from 11% to 20% on the SWE-bench Verified benchmark. 2. Reinforcement Learning Using Modified DAPO Building on Decoupled Advantage Policy Optimization (DAPO), several key modifications are introduced for scalability and stability: Asymmetric Clipping: Prevents collapse in policy entropy, maintaining exploration. Dynamic Sample Filtering: Focuses optimization on trajectories with actual learning signal. Length Penalties: Discourages excessive episode length, helping the agent avoid getting stuck in loops. Token-Level Averaging: Every token in every trajectory contributes equally to the gradient, empowering longer trajectories to influence updates. The agent utilizes a ReAct-style loop, which lets it combine reasoning steps with tool usage. Its supported toolkit includes arbitrary shell commands, precise code edits, navigation/search utilities, and a submit action to signal episode completion. Each interaction is grounded in a robust sandboxed environment, initialized from real repository snapshots and backed by a GitHub-style issue prompt. Scaling to Long Contexts and Real Benchmarks Initially trained with a context length of 65k tokens (already double that of most open models), performance stalls at 32%. A second RL phase expands the context to 131k tokens and doubles the episode length ceiling, focusing subsequent training on only the most beneficial tasks from the pool. This enables scaling to longer stack traces and diff histories inherent to real-world debugging and patching tasks. Results: Closing the Gap with Baselines The final RL-trained agent attains 39% Pass@1 accuracy on the SWE-bench Verified benchmark, doubling the rejection fine-tuned baseline, and matching the performance of cutting-edge open-weight models such as DeepSeek-V3-0324, all without teacher-based supervision. On held-out SWE-rebench splits, scores remain competitive (35% for May, 31.7% for June), indicating the method’s robustness. When compared head-to-head with top open baselines and specialized SWE agents, the RL agent matches or outperforms several models, confirming the effectiveness of the RL methodology in this domain. Pass@1 SWE-bench Verified Pass@10 Pass@1 SWE-rebench May Pass@10 Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct (RL, final) 39.04% 58.4% 35.0% 52.5% DeepSeek-V3-0324 39.56% 62.2% 36.75% 60.0% Qwen3-235B no-thinking 25.84% 54.4% 27.25% 57.5% Llama4 Maverick 15.84% 47.2% 19.0% 50.0% Pass@1 scores are averaged over 10 runs and reported as mean ± standard error. Key Insights Credit Assignment: RL in this sparse-reward regime remains fundamentally challenging. The paper suggests future work with reward shaping, step-level critics, or prefix-based rollouts for more granular feedback. Uncertainty Estimation: Real-world agents need to know when to abstain or express confidence. Techniques like output entropy or explicit confidence scoring are next steps. Infrastructure: Training utilized context parallelism (splitting long sequences over GPUs) on 16 H200 nodes, with distributed orchestration via Kubernetes and Tracto AI, and vLLM for fast inference. Conclusion This research validates RL as a potent paradigm for building autonomous software engineers using open-weight LLMs. By conquering long-horizon, multi-turn, real-environment tasks, the methodology paves the way for scalable, teacher-free agent development—directly leveraging the power of interaction rather than static instruction. With further refinements, such RL pipelines promise efficient, reliable, and versatile automation for the future of software engineering. Check out the Paper here. Feel free to check out our GitHub Page for Tutorials, Codes and Notebooks. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 100k+ ML SubReddit and Subscribe to our Newsletter. Star us on GitHub Sponsor us The post Nebius AI Advances Open-Weight LLMs Through Reinforcement Learning for Capable SWE Agents appeared first on MarkTechPost.